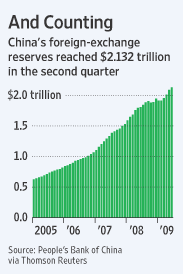
As far as currency traders are concerned, this development has two important implications, the first of which concerns the Chinese Yuan (also known as RenMinBi or RMB). A quick parsing of trade and capital flows data reveals that the majority of the $178 Billion came from unconventional sources. “The trade surplus was $34.8 billion in the second quarter and foreign direct investment was $21.2 billion.” Currency fluctuations (i.e. the depreciation in the Dollar relative to other major currencies) can explain a small portion, “leaving the bulk of the increase in the reserves unaccounted for.”
In short, most of the capital now flowing into China is so-called “hot money,” chasing a piece of the action in China’s surging property and stock markets. The benchmark stock index has risen 75% this year, making it the world’s best performer. In short, China is once again “caught in a squeeze similar to the one that bedevilled policymakers earlier this century, with a flood of hot money trying to force the government’s hand on the currency.” Either it allows the RMB to resume its upward path against the Dollar, or it raises interest rates rapidly to head off inflation. With the money supply now growing at an annualized rate of 30%+, the government is running out of time on this front.
The second implication concerns the composition of China’s reserves. You can recall that in recent months, Chinese officials have become more vocal about ending the Dollar’s role as the world’s reserve currency, and have even taken token steps towards achieving that goal. But the latest analysis suggests that when push comes to shove, China is still firmly behind the Dollar: “Estimates suggest around 65% of China’s official holdings are in U.S. dollar assets, and the remainder are denominated in euro, yen, sterling and other currencies. This mix has been relatively stable as the Chinese government continues to place the bulk of its reserves in U.S. Treasury securities.”
In fact, “stable” is an understatement. While other Central Banks are gradually paring their holdings of US Treasuries, China is adding to its own stockpile. Already the world’s largest holder of Treasuries, China added another $38 billion in May, for a total of $800 Billion. “On the contrary, Japan, Russia and Canada were sellers of US assets in May. Japan, the second-biggest international investor, reduced its total holdings by $8.7 billion to $677.2 billion.” Meanwhile, Zhou XiaoChuan, governor of China’s Central Bank has endorsed the current composition of reserves: “Despite the $800 billion in U.S. Treasuries, it is a diversified portfolio overall.” This certainly represents a step backwards for Mr. Zhou, who only a couple months ago was leading the charge for a global reserve currency.
Perhaps over the longer-term, it can begin to take steps to dislodge the Dollar, but for now, it appears that China has accepted the status quo. As one analyst observed, “We do expect China to increase its purchase of gold and other commodities over time, but these markets are just not big enough to make a meaningful dent in the structure of the overall FX holdings. For example, if China decided to hold 5 percent of its current $2 trillion reserves in gold, it would need to buy …the equivalent to about one year of world production. For other hard commodities, the cost of storage is high and prices fluctuate wildly.”
China did recently appoint a new official (an economist trained in the US) to manage its reserves. “The move isn’t likely to fluster foreign-exchange markets or herald any change in China’s exchange-rate policy and reform.” Still, Chinawatchers are advised to continue to monitor the situation closely for any signs of discontinuity.

July 17th 2009
Swiss National Bank Still Committed to FX Intervention
When the Swiss National Bank (SNB) intervened three weeks ago in forex markets, the Swiss Franc instantly declined 2% against the Euro. Since then, the Franc has risen slowly, and it’s now in danger of touching the “line in the sand” of 1.5 EUR/CHF that analysts have ascribed to the SNB.
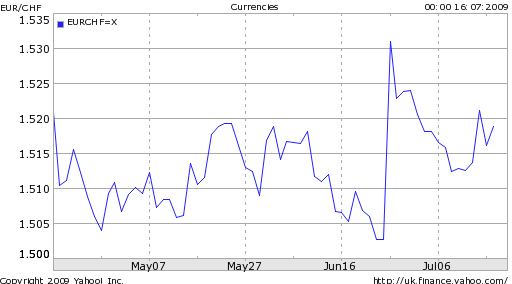
That’s not to say that the Central Bank lacks credibility. Quite the opposite in fact. Every time a member of the SNB speaks about the possibility of intervention, the markets react. For example, “Swiss National Bank Governing Board member Thomas Jordan said the central bank remains willing to intervene in currency markets to prevent a further appreciation of the Swiss franc..The franc declined against the euro after the remarks.” Also, “The Swiss National Bank is sticking decidedly to its policy to prevent an appreciation of the Swiss franc, SNB Chairman Jean-Pierre Roth said in an interview published on Friday…The Swiss franc dipped after Roth’s comments.”
In addition, given that the SNB premised its intervention on deflation fighting, its credibility is now higher than ever, since the latest figures imply an inflation rate that is well into negative territory: “Swiss consumer prices dropped 1 percent year-on-year in June, the same rate as in May when prices fell at their fastest rate in 50 years, underscoring deflation dangers although most of the drop was due to oil.” Despite a fiscal stimulus, coupled with an easing of monetary policy and quantitative easing, the Swiss money supply is barely growing. At this point, the only thing the SNB can do is (threaten to) manipulate its exchange rate.
Perhaps this is why traders are willing to push back against the SNB, backed by “foreign-exchange analysts [that] argue that the SNB won’t have an appetite to continue buying foreign currencies in large amounts much longer.” The SNB is also fighting against the perception that Switzerland is one of a handful of financial safe havens. The fact that the Swiss Franc is probably undervalued is also contributing to the steady inflow of capital into Switzerland.
Still, investors are afraid to step across the line. Futures prices for the EUR/CHF are all hovering slightly above 1.50, for the next 18 months. Prior to the latest round of intervention, the expectation was for a steady rise in the Swiss Franc.
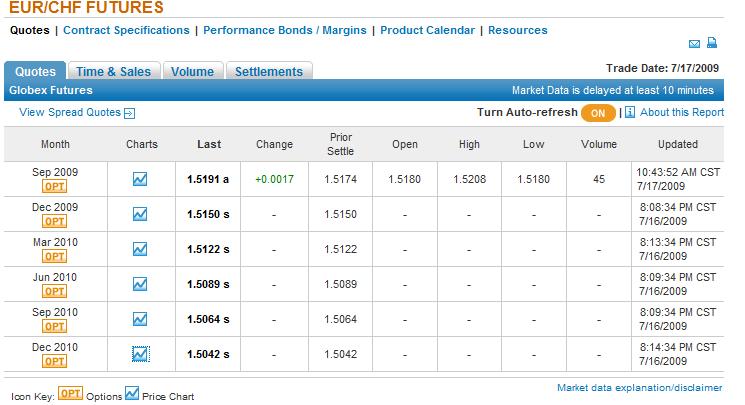
In addition, “There are significant options in place for the euro near the CHF1.50 level on the expectation the SNB will carry through another intervention if its resolve is questioned.” While the SNB would probably prefer a slight buffer zone, it will nonetheless rest assured as long as the Franc doesn’t appreciate further: “The SNB is just trying to stop the franc from becoming a one-way bet. ‘If the euro stays in the [current] CHF1.50 to CHF1.54 band, I think the SNB would be satisfied.’ “
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar